Tuning and Troubleshooting Transactional Replication – Kendal Van Dyke
From this video – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UBdAAvMMGwo
Types can be configured:
Central publisher (One Pub & DIS and multiple subscribers) – Common used
Central subscriber (On Sub, many DIS and many Bub) – This is mostly for data warehouse
Republishing subscriber (Pub –> Dis àSub/Pub àDIS àmultiple subscriber) – Ex: Pub & DIS are in datacentre 1 & multiple subscriber in DC 2
- Replication agent will not use SQL memory, it will use other buffer cache maybe OS or within SQL.
- It is recommended to have separate Publisher and Distributer for high transaction databases.
- For every DML command each transaction from publisher to subscriber will transfer as it is like single and single transaction. Ex: 1 million rows of transaction it will be 1 million write in the Publisher T log and Distributer T log and subscriber T log. You can avoid (OR trick is) this by doing this via stored procedure and replicate that SP execution by changing that option in publication property, so that it will execute the SP on publisher instead of sending that 1 million transaction.
- For making any alter table DDL for big tables, make sure to change the DDL changes to subscriber off in the publication property and manual do it on both side and start the distributer agent.
- Check publication property and you can learn more on it. (Ex: each table and SP property , you can change as per your environment etc)
- You can replicate SP with execution, UDF & View definition, Indexed view with data & DDL as well.
- You can replicate indexed view with data not in GUI but from T-SQL, script out the replication and make changes in the script @type = ‘Indexed view schema only’ to ‘Indexed view logbased’
- You can do both vertical(If you remove columns from article property that is vertical filtering) and horizontal filtering (If you add where condition that is horizontal). It is recommended to do for actively changing table only for horizontal filtering. Beware, even if you remove columns in table still the replication will look whole tables only for its action.
- Subscriber model push is – Distributer agent on it is own or publication side pull is for subscriber side
- Synchronization – By default is automatic, for big table across the WAN you can use initialize with backup – need to learn and test this.
- Enable Sync with backup option for distributor– it is good option for distributer but the transaction log in publisher will grow big larger than expected. Other issue, until T log backup completes on publisher the data will not be replicated. There will be latency.
Query to check and enable Sync with backup option for distributor:
select DATABASEPROPERTYEX (‘distribution’,’issyncwithbackup’)
Execute sp_replicationdboption @dbname =’distribution’, @optname=’sync with backup’, @value =’true’
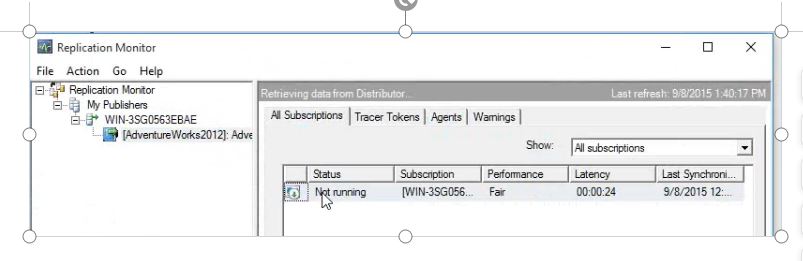
- Monitoring the replication
In all subscription tab – You can double click all subscription to view details and status. Do not double click the undistributed commands. It might take more time to return your transaction.
Tracer tokens are to measure the latency, it is useless, you can do that by script. Check google.
Agent – You can double click each agent and view history and start and stop agent as well. There is calling from SQL agent job
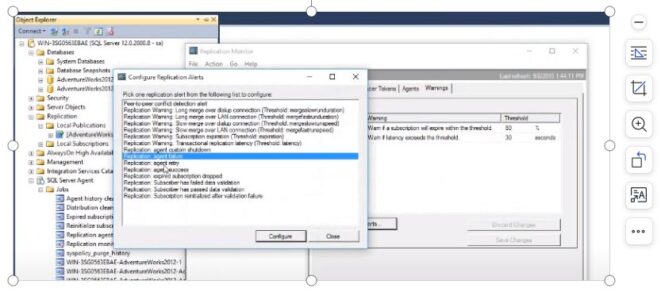
Warning – When you have problem with replication, you can configure the alert here. Mostly for two items (replication agent failure and agent retry). It is same as alters in SSMS. In the option tab change the delay between response at least 5 minutes and enable it, default it will not enabled.
You can monitor all by T-SQL:
sp_helppublication
sp_helparticle
sp_replcounters
Permon counters
SQLserver: Replication agents
SQLserver: Replication Dist.
SQLserver: Replication Logreader
SQLserver: Replication Snapshot
Distribution DB tables:
MSarticles
MSpublications
MSsubscription
MSagent_profiles
MSdistribution_agents
MSlogreader_agents
History
MSdistribution_history
MSlogreader_history
You can use this and write query to find out how many commands are written per day / hours etc. Check google and find out code.
Also, increase the distributor history from default 48 hours to higher. By right click replication à Distributer property.
- Replication agent profile tweaking configuration
Replications monitor à Agent à Right click the agent àAgent profile à You can change any value based on your environment
Replications monitor à All subscription à Agent profile à Continue on data consistency error à skip error. You can skip known errors. There are lot of options you can change in the agent from default to your environment.
- Subscription Stream
It is introduced from SQL 2008. This parameter helps to reduce the latency when moving data from Distributor to Subscriber by using multiple parallel writer threads. It is only applicable for Distribution Agent. It is also known as Distribution Agent SubscriptionStreams parameter.
It is easy to configure à Open the distributer agent job in SQL agent – In step 2 add in the last –subscriptionstreams 8
From this video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m28K21Widn0
ServerA- Pub ServerB- Sub ServerC- Dist
- Monitor the replication from extended events
Bulk insert, Statement completed, RPC completed